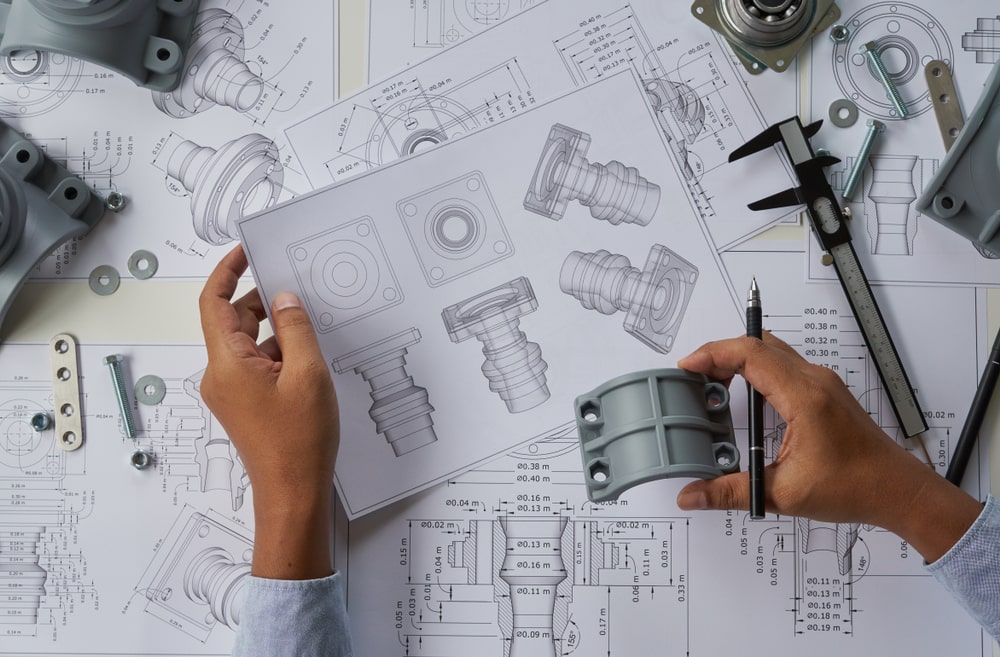
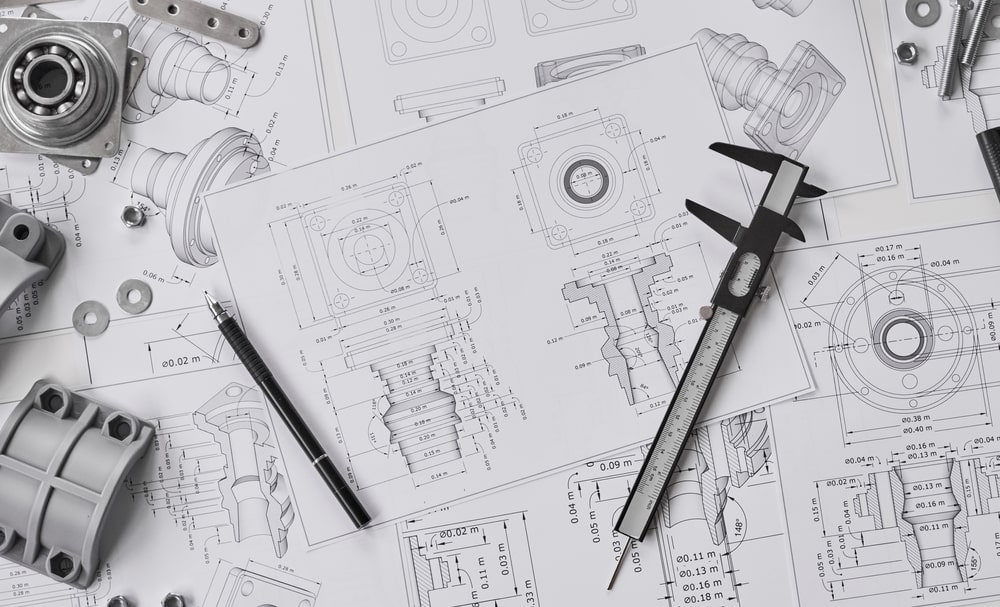
Description
“Custom Engineered Components” is a broad term that generally refers to specialised and tailor-made parts or elements designed for specific applications in various industries. These components are engineered to meet unique requirements, specifications, or challenges that off-the-shelf or standard components may not adequately address. The term can be applied across a wide range of fields, including manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, electronics, and more.
Here are some key aspects and considerations related to custom engineered components:
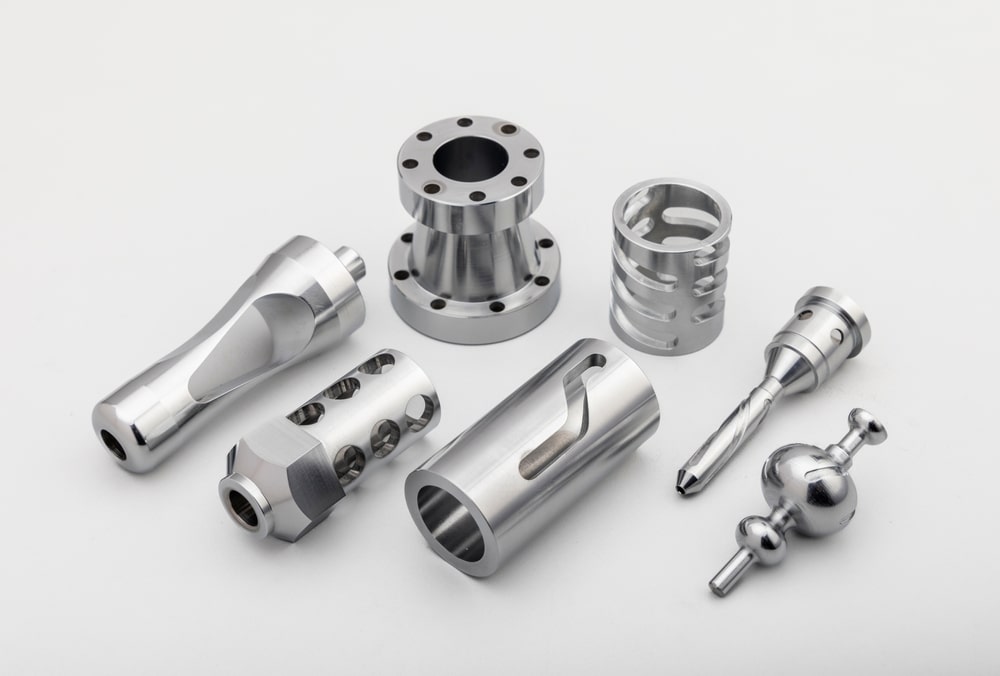
Tailored Solutions: Custom engineered components are designed and manufactured to fit specific needs or solve particular problems. This can involve factors such as size, shape, material composition, tolerances, and performance characteristics.
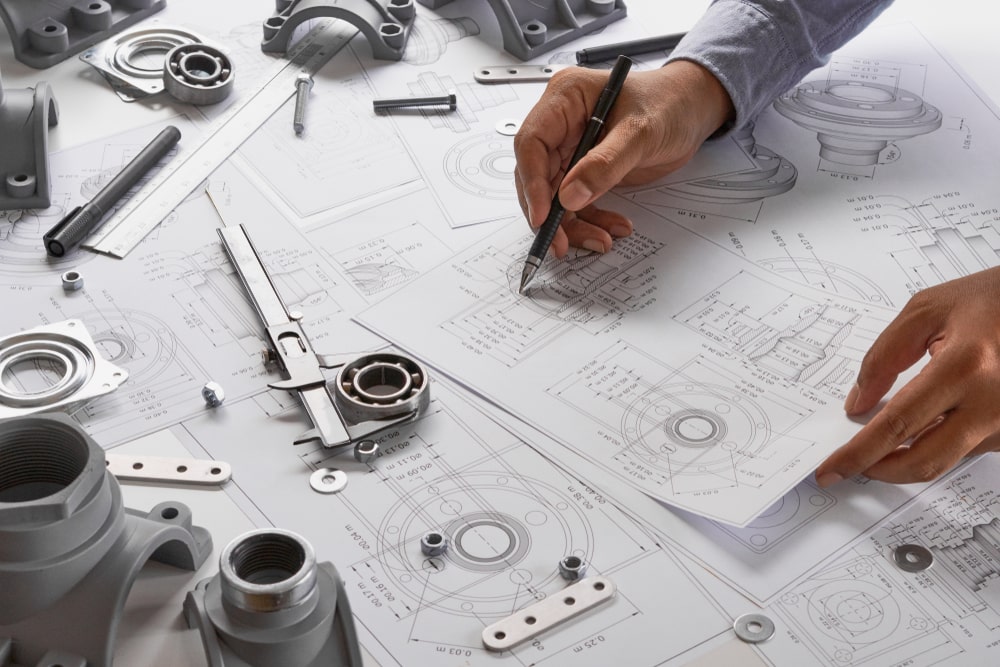
Precision Engineering: The design and production of custom components often involve precise engineering to ensure that they meet exact specifications. This may include detailed CAD (Computer-Aided Design) modeling, simulation, and prototyping to achieve the desired outcome.
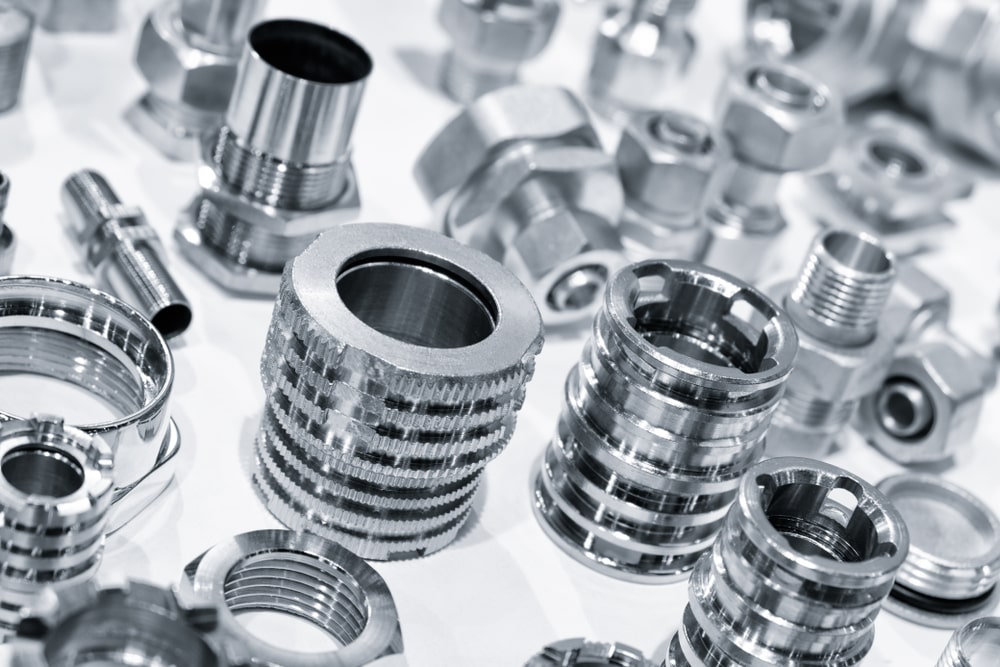
Materials: Depending on the application, custom components can be made from a variety of materials, including metals, plastics, composites, and specialised alloys. The choice of material is crucial to achieving the desired performance, durability, and other relevant properties.
Manufacturing Processes: Custom engineered components may be produced using various manufacturing processes such as machining, injection moulding, 3D printing, casting, and more. The selection of the manufacturing method depends on the complexity of the component and the desired properties.
Industry Applications: These components find applications in diverse industries. For example, in aerospace, custom engineered components may be critical for lightweight and high-strength requirements. In the medical field, custom components may be designed for specific medical devices. Similarly, in automotive manufacturing, custom components can play a role in enhancing vehicle performance.
Prototyping: Before mass production, it’s common to create prototypes of custom components to test their functionality and suitability. This helps identify and address any issues before full-scale production.